


NIST’s mission is to “promote the progress of science and technology for the benefit of society.”
NIST was founded in 1901 as the National Bureau of Standards (NBS). In 1988, NBS was renamed NIST to reflect its broader mission. NIST is headquartered in Gaithersburg, Maryland, and has laboratories and offices throughout the United States.
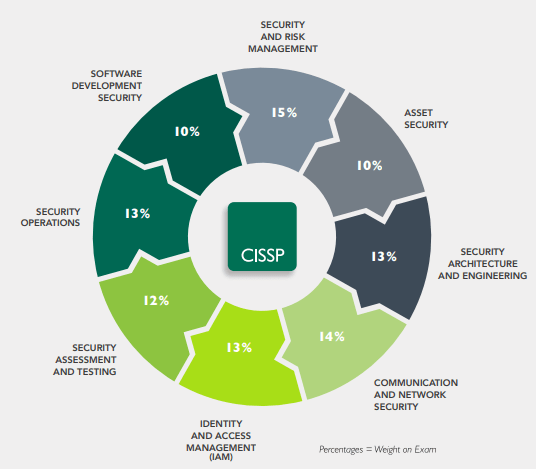
NIST’s work is divided into four main areas:
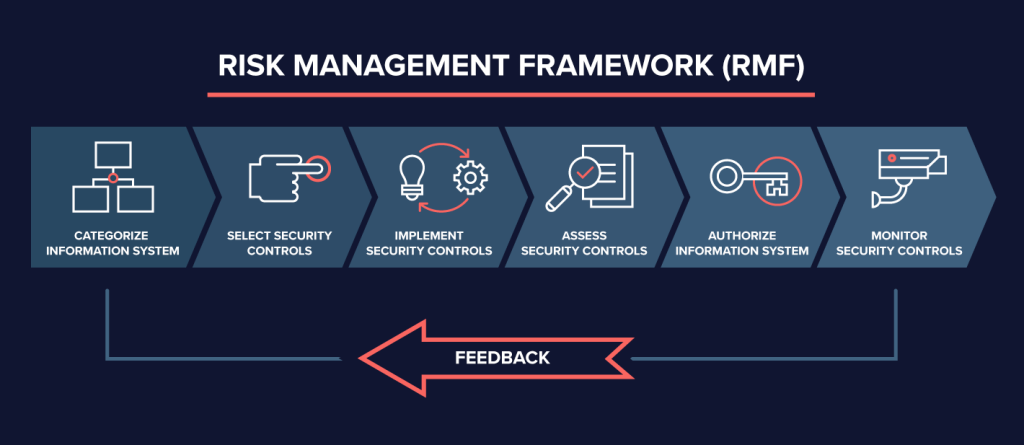
The RMF is based on the following principles:
The RMF is a valuable tool for organizations that are looking to improve their information security posture. The RMF can help organizations to identify and mitigate risks, protect their information and systems, and comply with regulations.
The RMF is made up of the following five steps:
The RMF is a continuous process that should be updated as new risks emerge and new controls become available. The RMF is a valuable tool for organizations that are looking to improve their information security posture.
IAM helps organizations to ensure that only authorized users have access to sensitive data and systems.
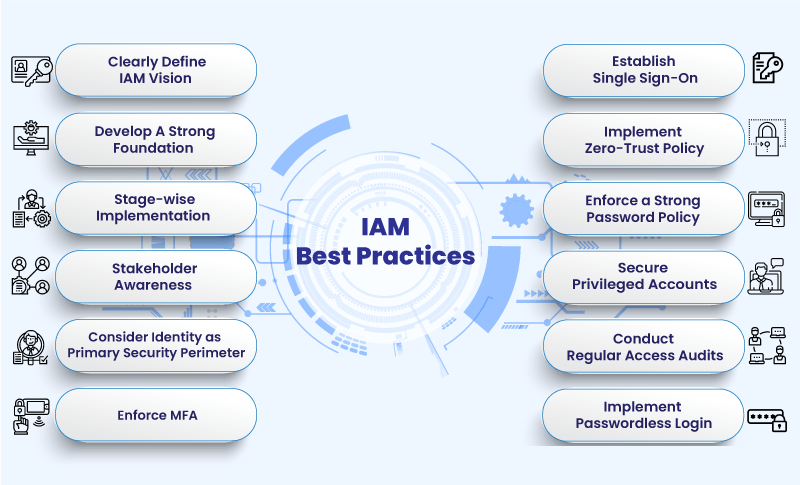
IAM typically includes the following features:
IAM is an important part of an organization’s overall security strategy. IAM can help organizations to protect their data and systems from unauthorized access.
Here are some of the benefits of implementing IAM:
IAM is a valuable tool for organizations of all sizes. IAM can help organizations to improve their security posture, increase their efficiency, and reduce their costs.