There are many Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) tools and software available in the market.
Some of the best IDS tools include Snort, Suricata, Bro, OSSEC, and Security Onion1.
Snort is a free and open-source network-based IDS software that provides opportunities for automated and manual threat hunting1.
Suricata is an open-source network-based IDS software that can detect network intrusions in real-time2.
Bro is an open-source network-based IDS software that can detect intrusions by analyzing network traffic1.
OSSEC is an open-source host-based IDS software that can detect intrusions by analyzing system logs1. Security Onion is a Linux distribution for intrusion detection, network security monitoring, and log management1. Intrusion detection systems (IDSs) tools and softwares
An Intrusion Detection System (IDS) is an application that monitors network traffic and searches for known threats and suspicious or malicious activity.
The IDS sends alerts to IT and security teams when it detects any security risks and threats1.
Most IDS solutions simply monitor and report suspicious activity and traffic when they detect an intrusion1.
Some IDS are capable of taking actions when malicious activity or anomalous traffic is detected2.

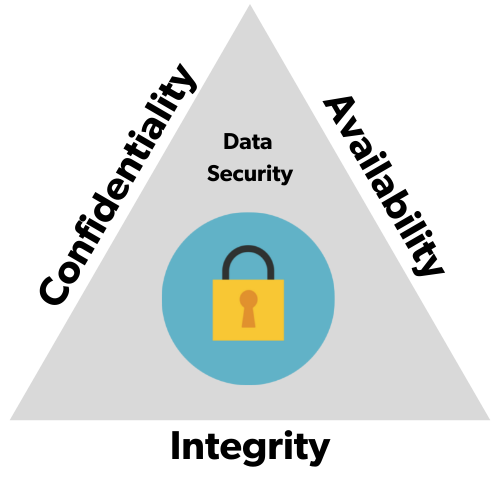
The CIA (Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability) triad is a widely used information security model that can guide an organization’s efforts and policies aimed at keeping its data secure.
Confidentiality refers to preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure.
Integrity refers to maintaining the accuracy and consistency of data over its entire life cycle. Availability refers to ensuring that authorized users have access to information and associated assets when required.
Examples of Confidentiality include encryption, access controls, and non-disclosure agreements. Examples of Integrity include checksums, digital signatures, and version control. Examples of Availability include redundant systems, backups, and disaster recovery plans1. Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability (CIA) Triad examples.

It was founded in 2001 by Mark Curphey and Denise Groves, and is headquartered in Maryland, USA. OWASP has over 100,000 members worldwide, and its mission is to “make software security everyone’s business.”
OWASP provides a variety of resources to help developers, security professionals, and businesses improve the security of their software. These resources include:
OWASP also hosts a variety of events, including conferences, trainings, and hackathons. These events provide opportunities for developers, security professionals, and businesses to learn about and discuss security issues.
OWASP is a valuable resource for anyone who is interested in improving the security of their software. Its resources are free and open to everyone, and they can help you to make your software more secure.
Here are some additional information about OWASP:

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) provides a policy framework of computer security guidance for how private sector organizations in the United States can assess and improve their ability to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber attacks.
The CSF consists of five functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover2. The Identify function is used to develop an organizational understanding of managing cybersecurity risk to systems, people, assets, data, and capabilities.
The Protect function is used to develop and implement appropriate safeguards to ensure delivery of critical infrastructure services.
The Detect function is used to develop and implement appropriate activities to identify the occurrence of a cybersecurity event.
The Respond function is used to develop and implement appropriate activities to take action regarding a detected cybersecurity event.
The Recover function is used to develop and implement appropriate activities to maintain plans for resilience and to restore any capabilities or services that were impaired due to a cybersecurity event.
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cyber Security Framework (CSF) functions and roles examples.
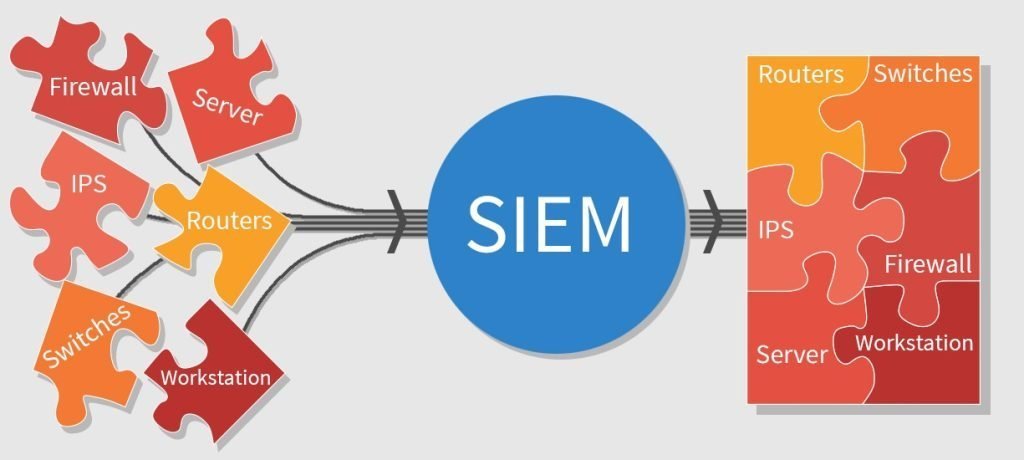
Security information and event management (SIEM) is a security solution that collects, aggregates, and analyzes security logs and events from various sources, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDSs), and web application firewalls (WAFs). SIEM solutions can be used to identify security threats, investigate security incidents, and comply with security regulations.
SIEM solutions typically have the following features:
SIEM solutions can be a valuable tool for organizations of all sizes. They can help organizations to identify security threats, investigate security incidents, and comply with security regulations.
Here are some of the benefits of using a SIEM solution:
If you are looking for a way to improve your organization’s security, a SIEM solution may be a good option for you.

Sensitive personally identifiable information (SPII) is a type of personal information that, if lost, stolen, or disclosed without authorization, could result in significant harm, embarrassment, inconvenience, or unfairness to an individual. SPII requires stricter handling guidelines because of the increased risk to an individual if the data is inappropriately accessed or compromised.
Some examples of SPII include:
SPII can be collected and used by a variety of organizations, including businesses, government agencies, and healthcare providers. It is important for organizations to take steps to protect SPII from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. These steps may include:
By taking these steps, organizations can help to protect SPII and the individuals whose information it represents.
